Metal forging is a method that uses compressive pressures to shape and form metals. Cold forging, warm forging, and hot forging are three procedures distinguished by the temperature of the metal. Read More…
For over 30 years, we have provided metal forged products for a wide variety of industries, including the aerospace, military, food service, medical, and automotive industries. Our customers know they can trust our forgings for quality and affordability.
Although we have over 100 years of experience, we are committed to continually expanding our offerings in all industries. We are not content to remain as we are, but we continually work to improve our products and processes each and every day.
All Metals & Forge Group is your ISO9001:2015 and AS9100D registered forging facility. All Metals provides a wide range of materials, products and services, including discs, shafts, sleeves, cylinders, plates, blocks and many other shapes, both stock and custom, satisfying all of their customers’ requirements. Give All Metals & Forge Group a chance to satisfy your needs— you’ll be glad you...
Welcome to Edgerton Forge, Inc., where we specialize in the production of high-quality forgings for a wide range of industries and applications. With a rich history spanning decades and a steadfast commitment to excellence, we have established ourselves as a trusted leader in the forging industry.

Trenton Forging is a QS 9000 producer of high-quality closed impression die steel forgings including steering and suspension parts, engine parts, construction and mining parts, and many more from carbon and alloy steel. For more information please call Trenton Forging today!

More Metal Forging Companies
What is Metal Forging?
Forging is one of the most important metalworking operations in the metal manufacturing sector. It's especially important in the iron and steel industries, where it is seen as a huge productivity boost.
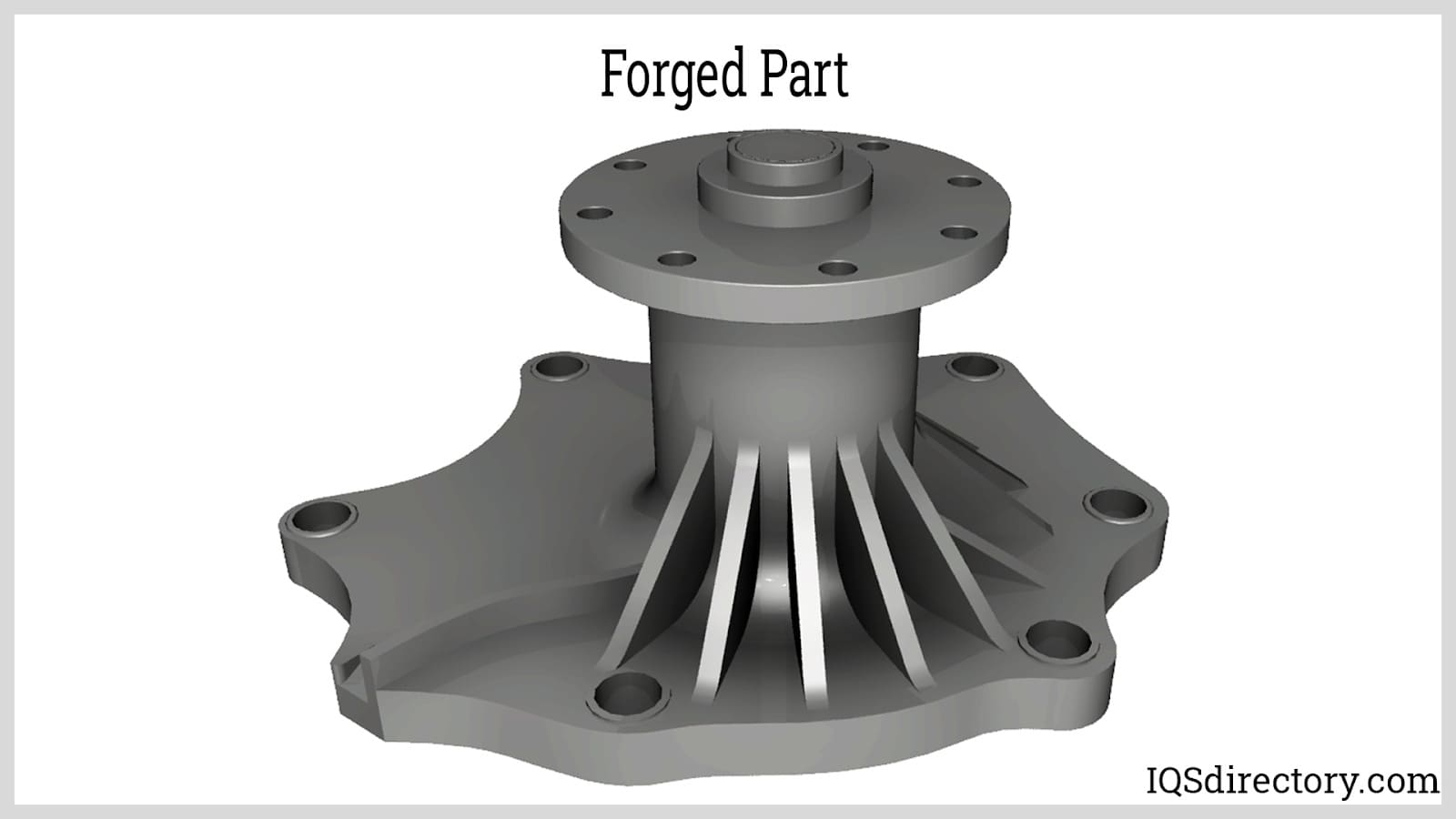
Metal Forging Processes
The metal forging processes include:
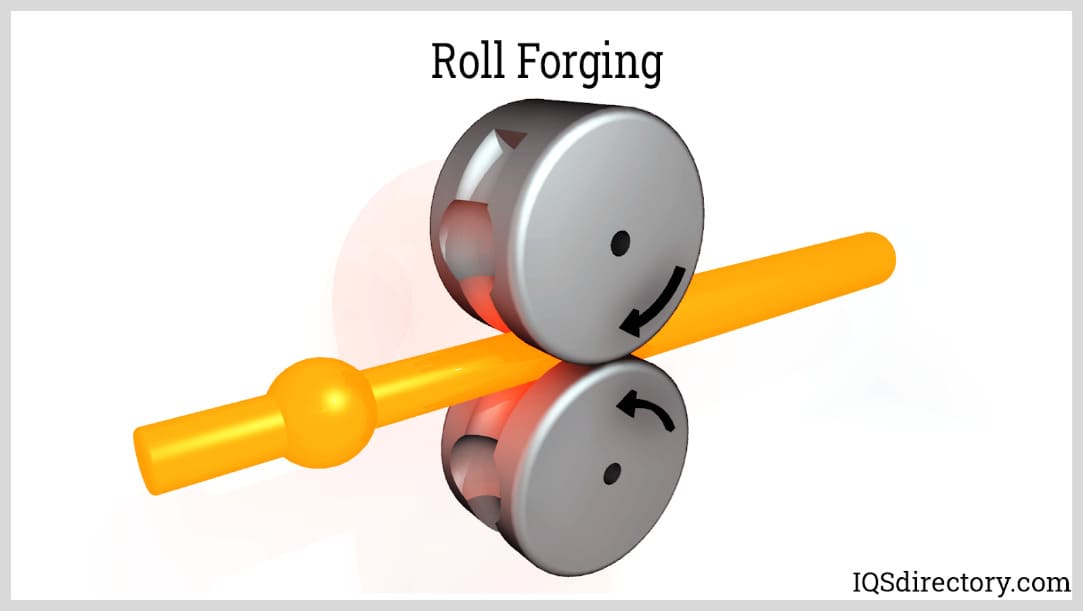
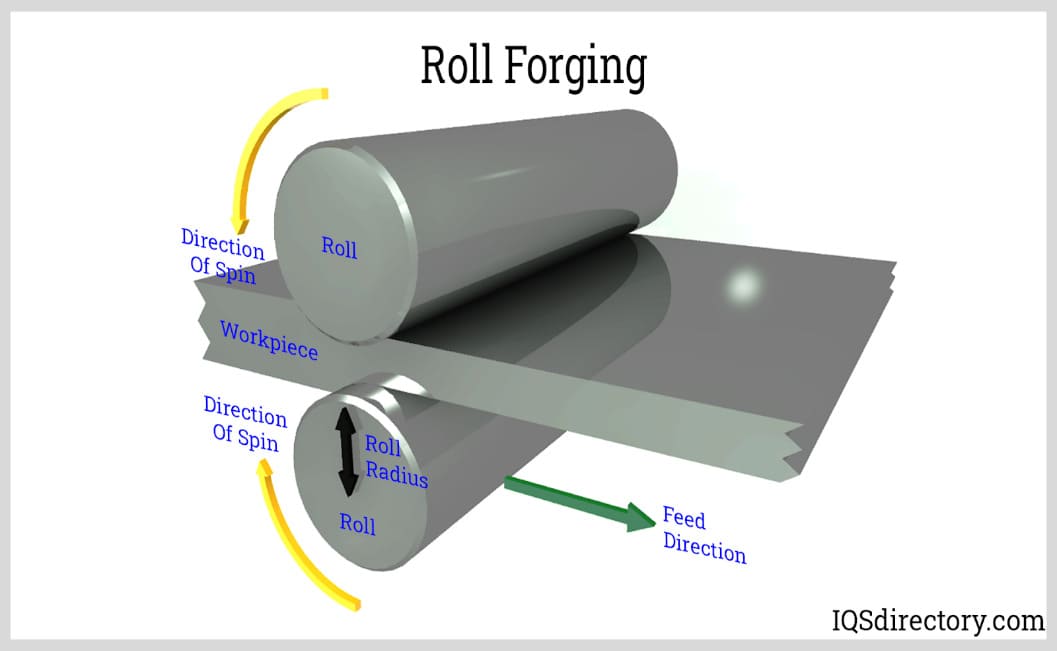
Roll Forging
Roll forging, also known as roll forming, is a forging technique that involves producing a metal object with opposing rollers. Although roll forging uses rolls to create parts and components, it is still classified as a metal forging rather than a rolling process. This procedure uses two cylindrical or semi-cylindrical horizontal rolls to distort a round or flat bar stock. The thickness is lowered while the length is extended due to this activity.
The mechanical qualities of parts produced by roll forging are superior to those produced by many other methods. A hot bar is transferred between the two rolls once it is placed. Then, it is gradually shaped while rolling through the machine's formed grooves. These grooves' perfectly formed geometry is what forges the part to the desired dimensions. Roll forging is frequently utilized in the automotive sector to make parts. Knives and hand tools are among the items made from it.
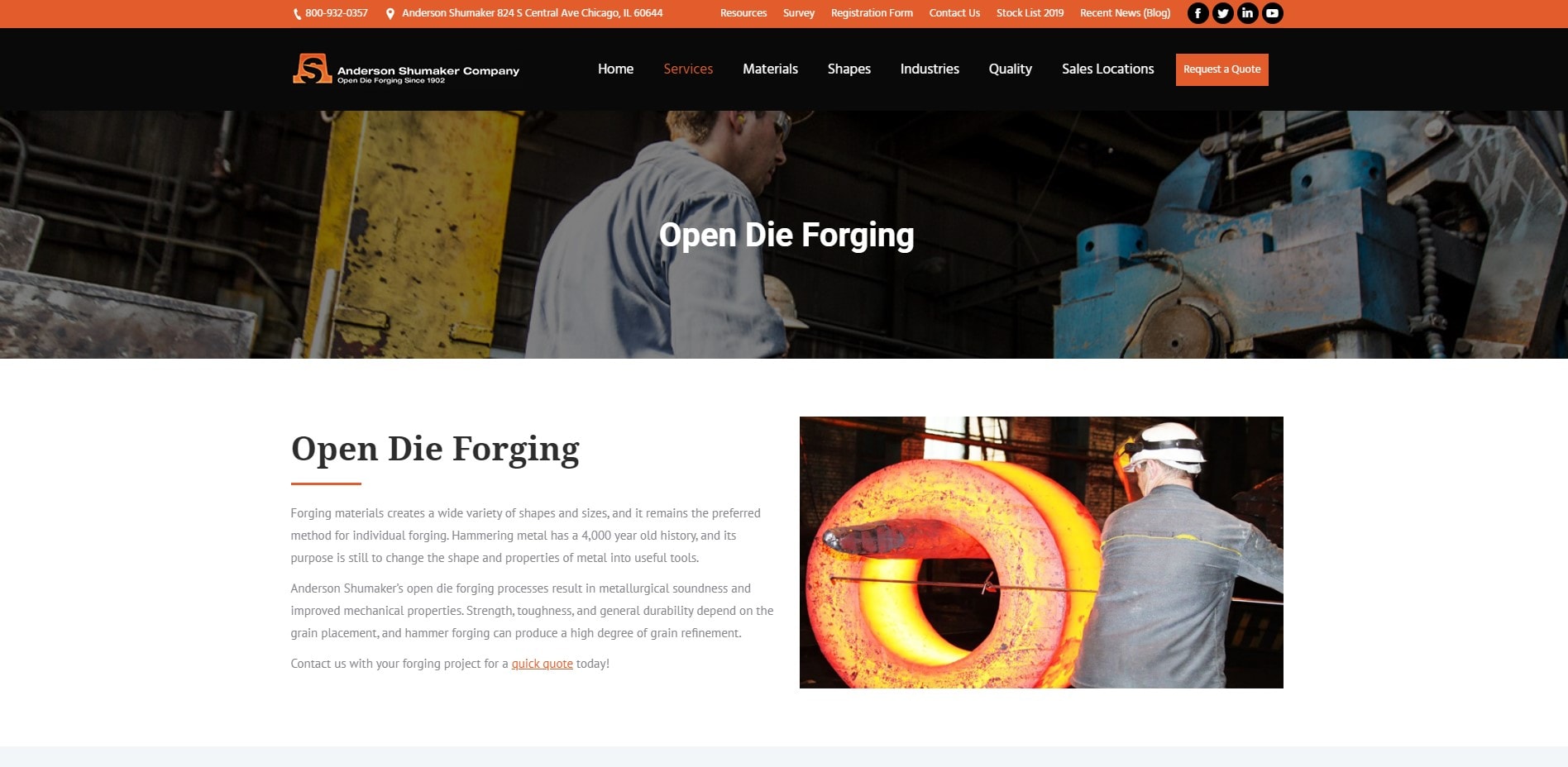
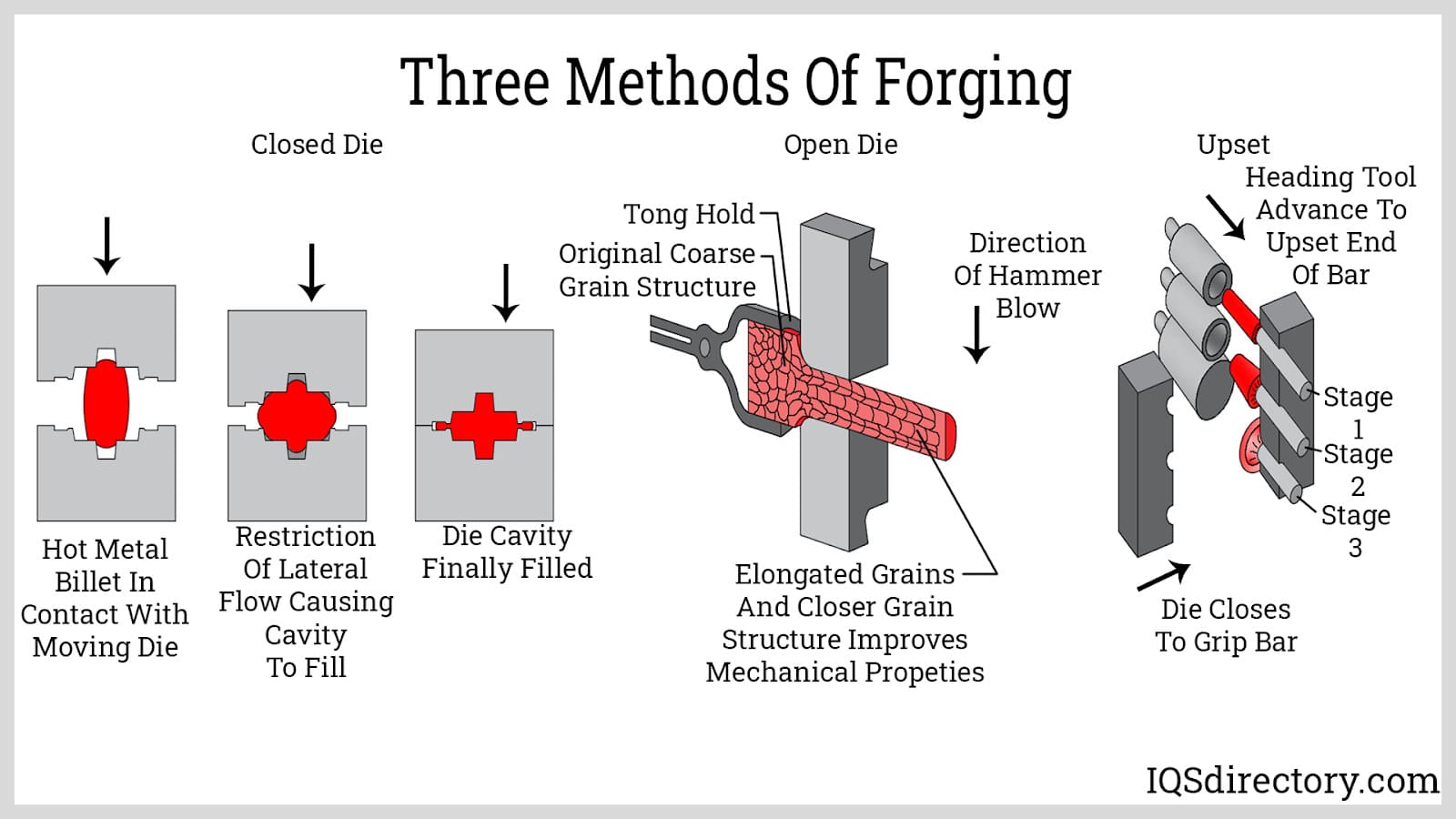
Open Die Forging
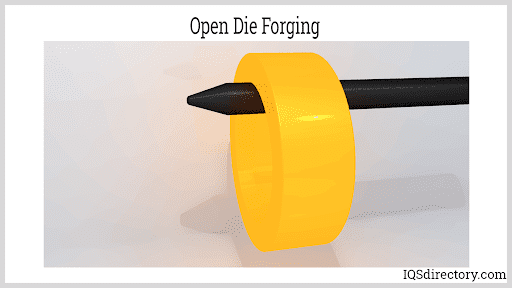
Heated metal components are formed between a top die attached to a ram and a bottom die attached to a bolster, anvil, or hammer in open die forging. Metal is never totally enclosed or restricted in open die forging dies. Temperatures vary from 500 °F to 2400 °F (260 to 1315 °C), depending on the metal parts involved in the process. The intricate hammering, or pressing of the workpiece, is undertaken after the metal has been properly heated to progressively mold the metal to its desired form. The open die forging procedure is most commonly employed to make larger, simpler-shaped pieces like bars, rings, and hollows.
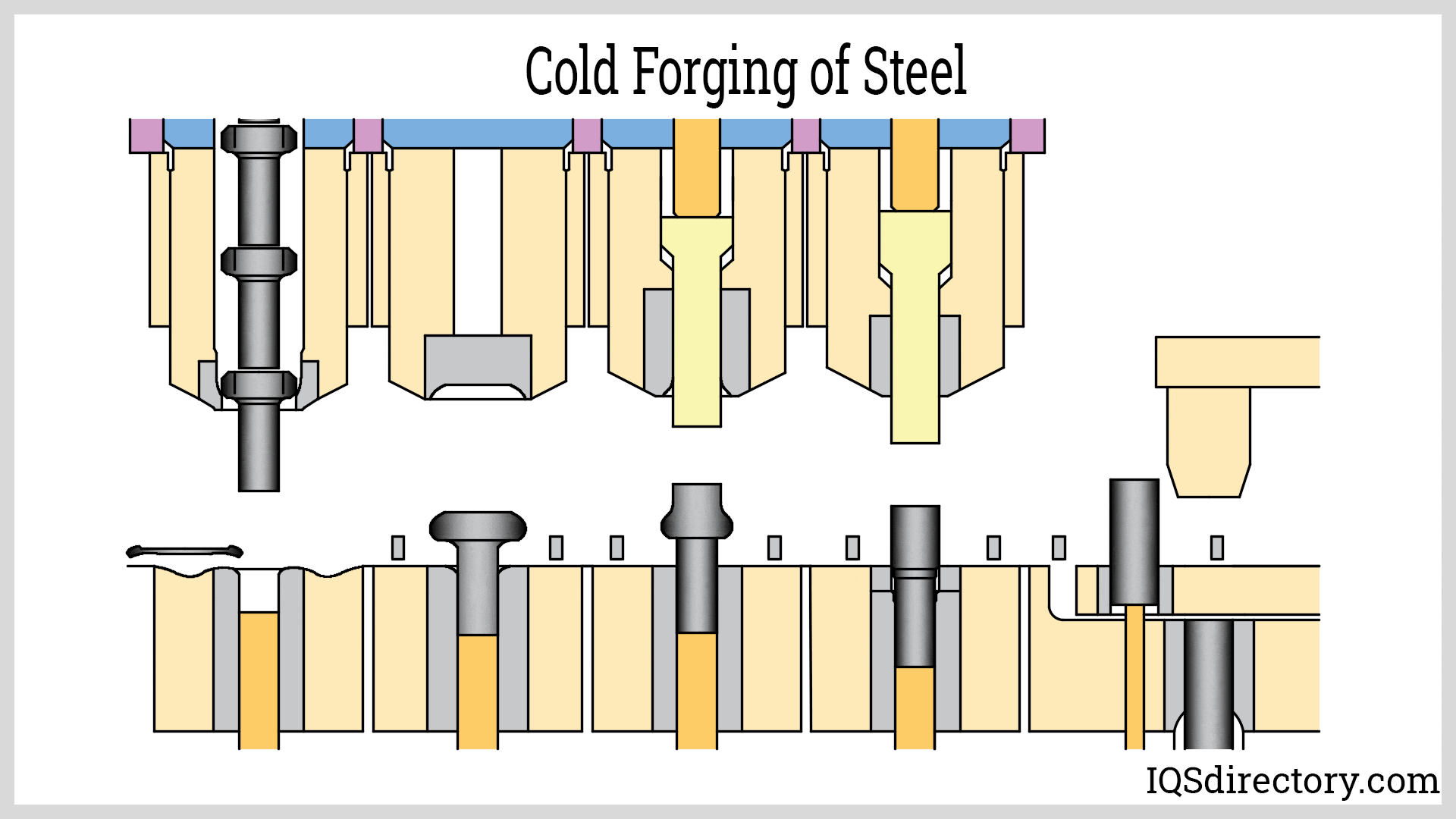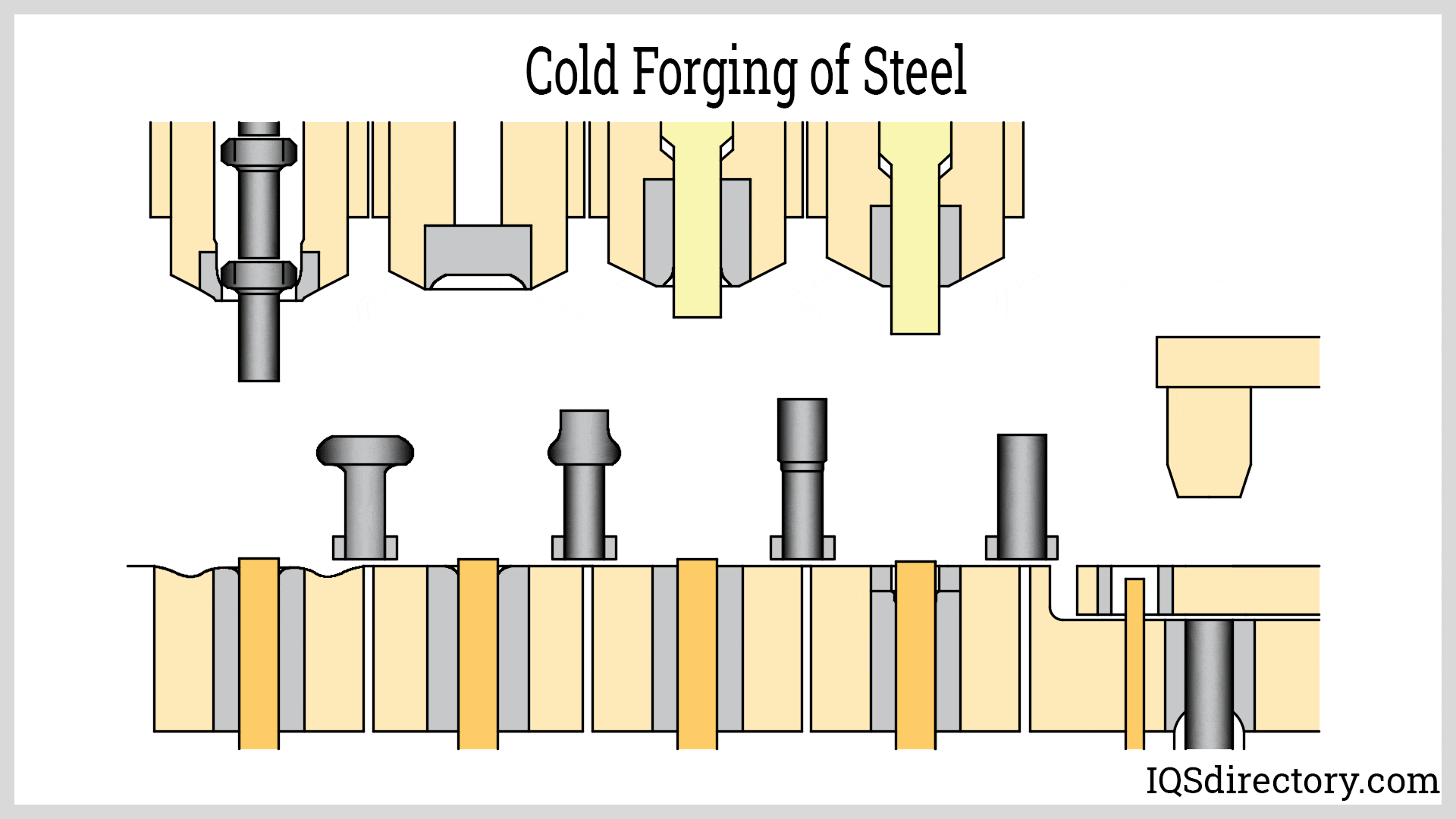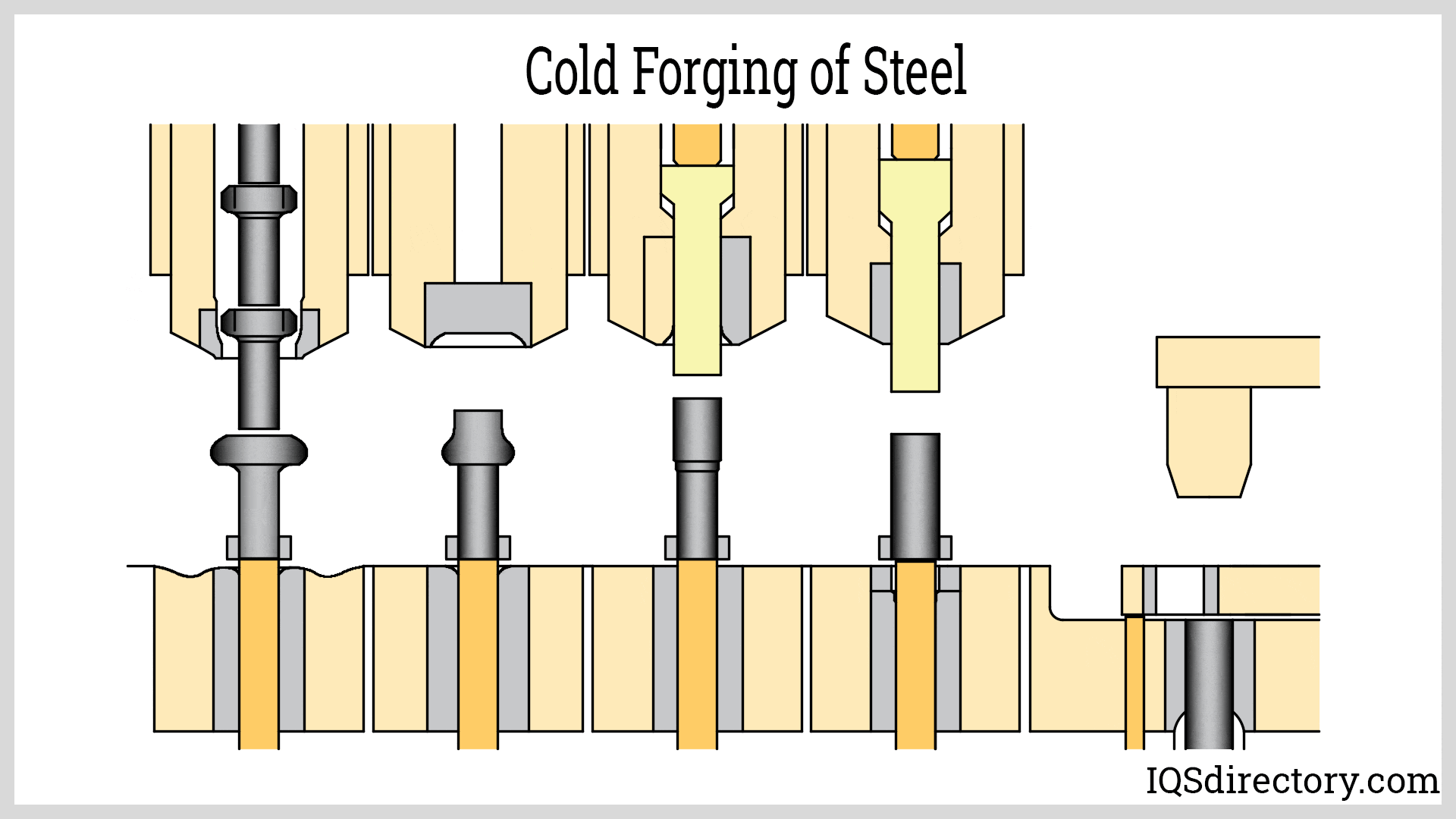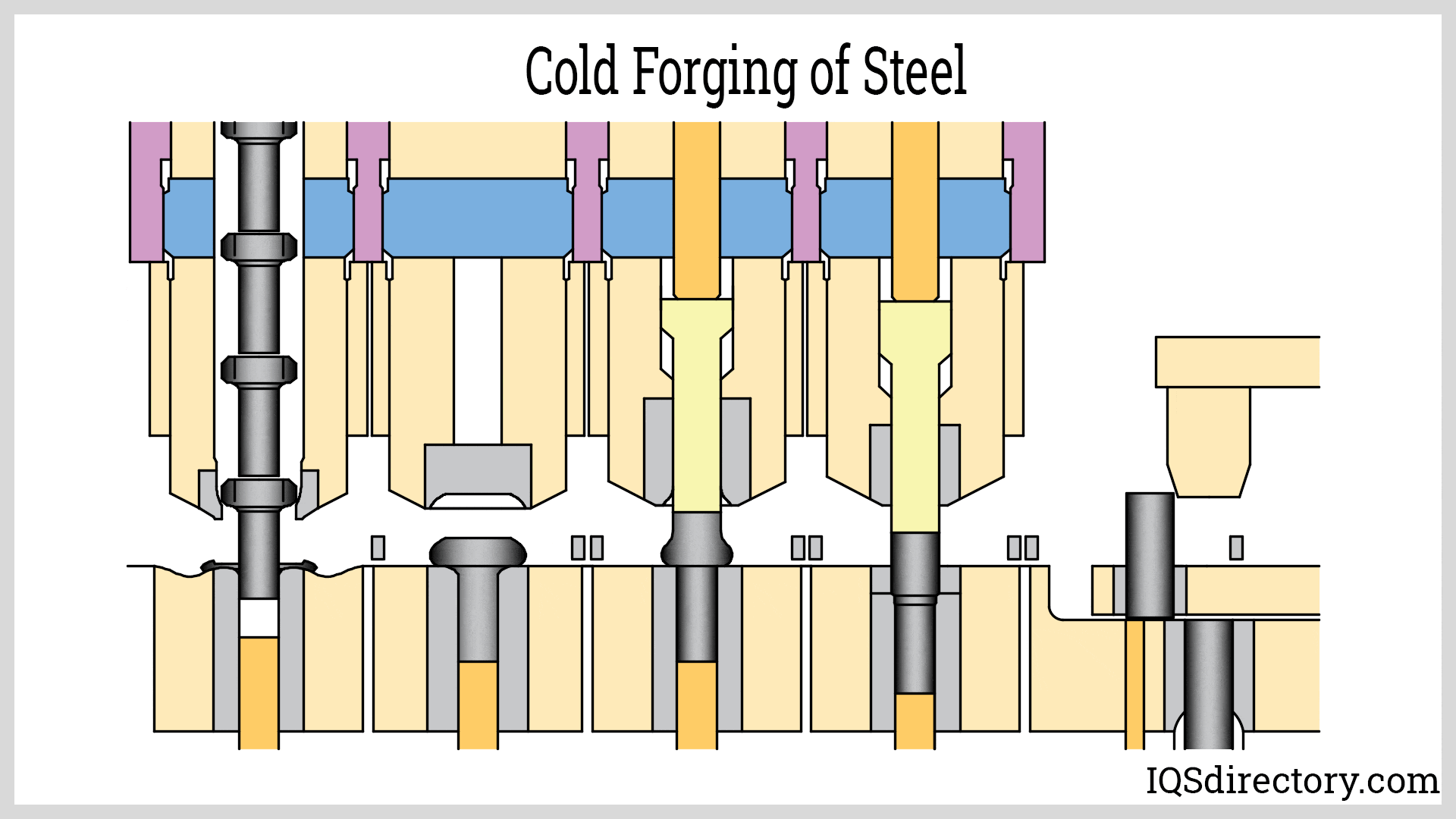
Closed Die Forging
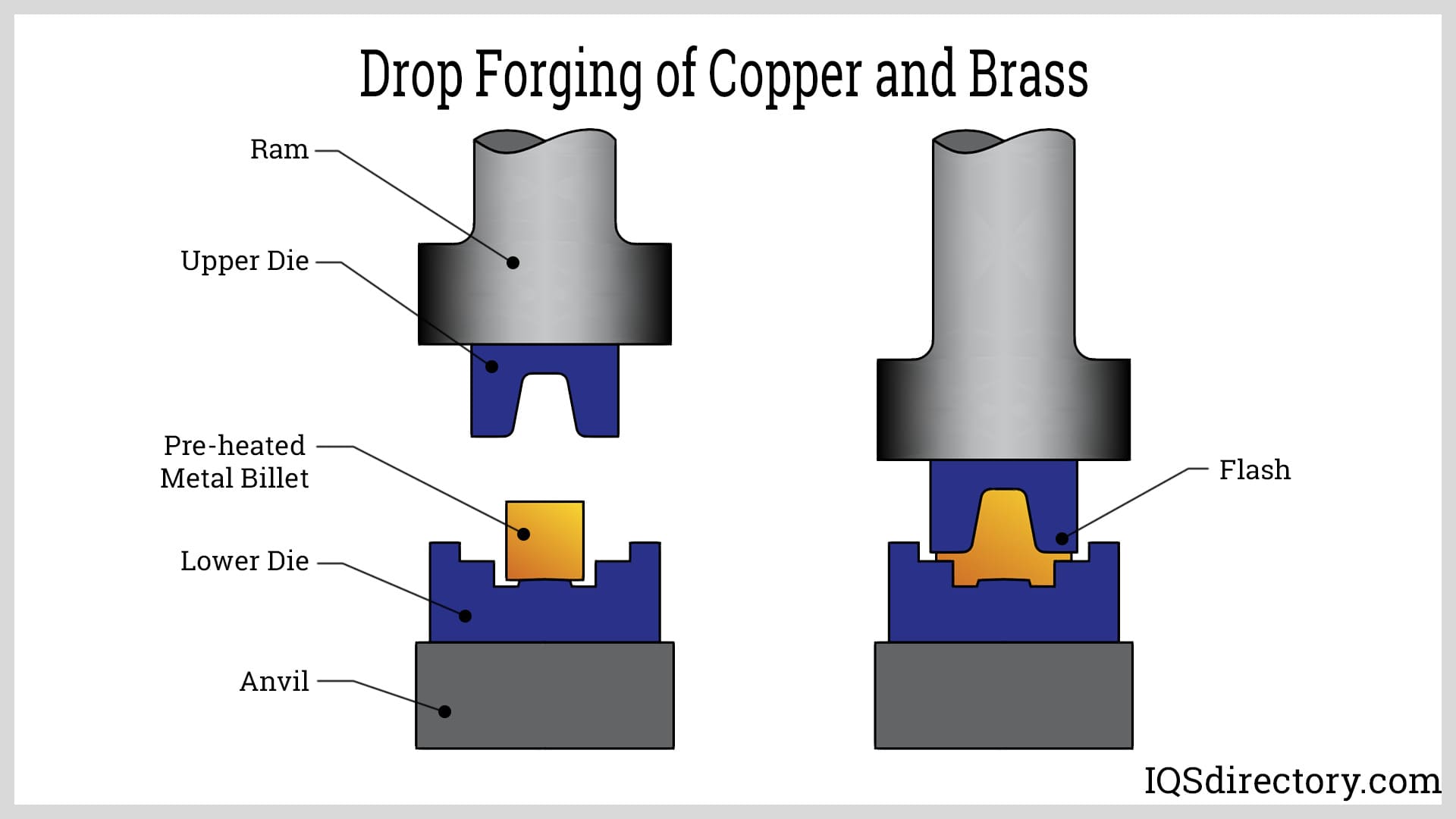
The top and bottom die move towards each other, forcing the metal into the shape they possess. The metal is placed onto the bottom die and is covered completely or partially when the dies meet. The forging shape is incorporated as a negative image on the top or bottom die. This method may produce items weighing anywhere from a few ounces to 60,000 pounds (27 metric tons).
Metal Forging Equipment
The metal forging equipment include:
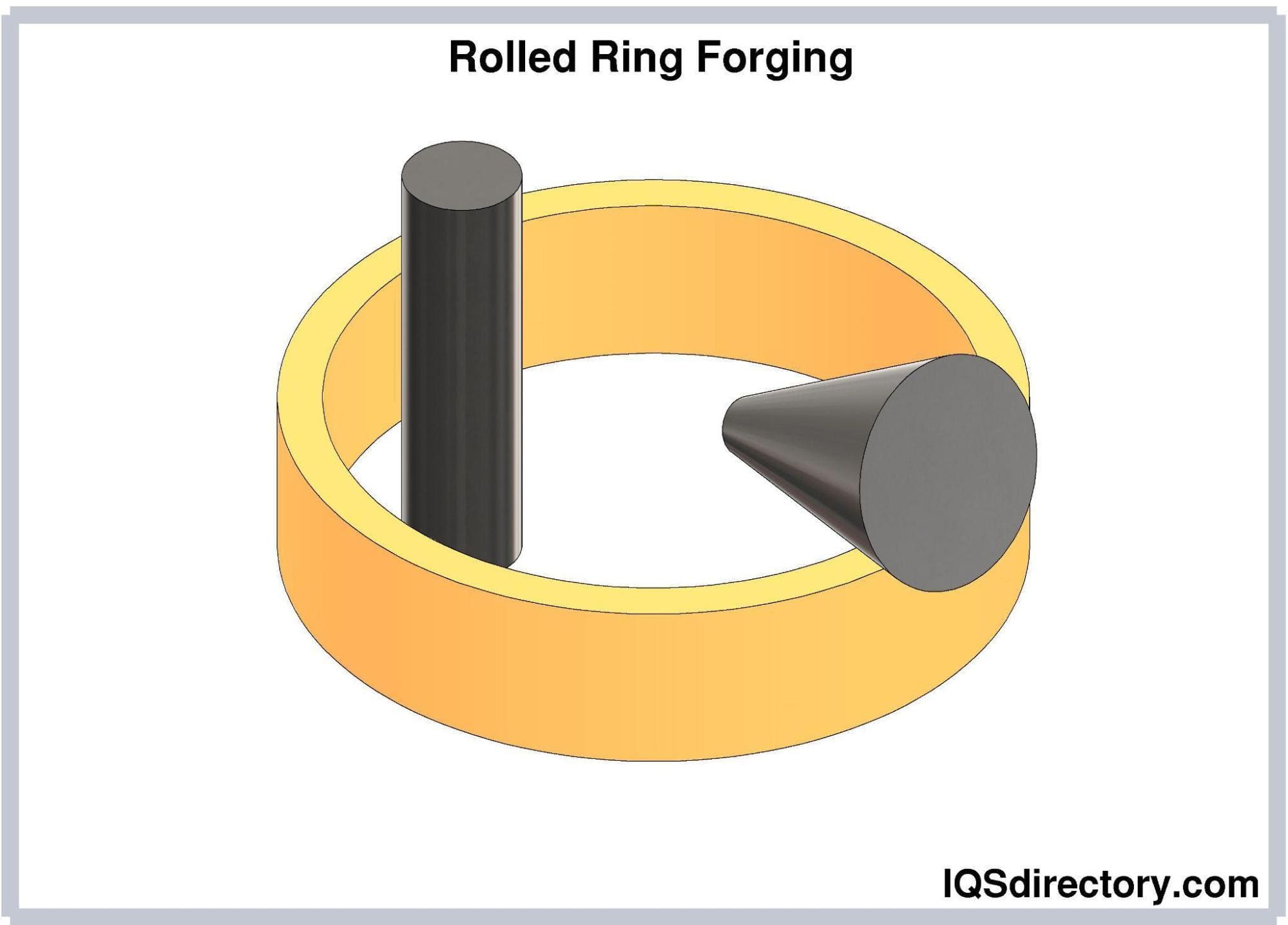
Ring Rollers
Ring rollers can make rings with diameters ranging from a few inches to more than 300 inches (762 cm). Ring rollers form a single-piece ring, eliminating the need for welding. Instead, it uses pressure to rotate a hollow round piece of metal against a rotating roll.
Upsetters
The fundamental distinction between upsetter and press forging is that an upsetter is a forging press that is employed horizontally. Instead of pressing metal downward into a die, the metal is pushed horizontally into the die impression.
Hammers
The hammer, sometimes known as a power hammer, is an instrument used mostly for forging. The hammer is used to beat the metal to distort it. The hammer is either a hand-held hammer or a gigantic power hammer. A hammer may pound metal into shape if it has a driving power of 50,000 pounds and can produce high-pressure impact strikes.
Presses
Presses use either mechanical or hydraulic pressure to provide continuous pressure on forging dies. To vertically crush metal into die cavities with controlled high pressure, this machine requires a 50,000-ton driving force. Rather than constantly hammering the metal to distort it, the metal is slowly forced into the dies.
How Forging Strengthens Metals
During forging, minor cracks are fixed and empty areas in the metal are filled as the metal is heated and pressed. Furthermore, the hot forging process breaks up any metal imperfections and redistributes them throughout the metalwork.
As a result, the forged portion contains far fewer inclusions. In addition, compound compounds incorporated in steel during the manufacturing process provide stress areas in the product. Although impurities should be handled during the initial casting process, this step refines the metal.
Another method that forging strengthens metal is by changing the grain structure. This has to do with the grain flow of the material when it deforms. A desirable grain structure can be generated, similar to other forming techniques, making the forged metal stronger.
Choosing the Correct Metal Forging Supplier
To ensure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing metal forgings from a metal forging supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of metal forging suppliers. Each metal forging supplier has a business profile page illustrating their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each metal forging business website using our proprietary website previewer to quickly learn what each business specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple metal forging companies with the same form.





 Die Castings
Die Castings Forgings
Forgings Grey Iron Castings
Grey Iron Castings Investment Castings
Investment Castings Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services